FinkAvenue
Investment thesis
The anticipated recession in the U.S. may hit even the most stable businesses. Therefore, we do not see a good entry point for Visa (NYSE:V) right now. There is ample reason to revise the forecast of the transactional systems sector downwards due to evolving competition caused by emergence of alternative methods of payment and impending recession.
The new model of consumer loans
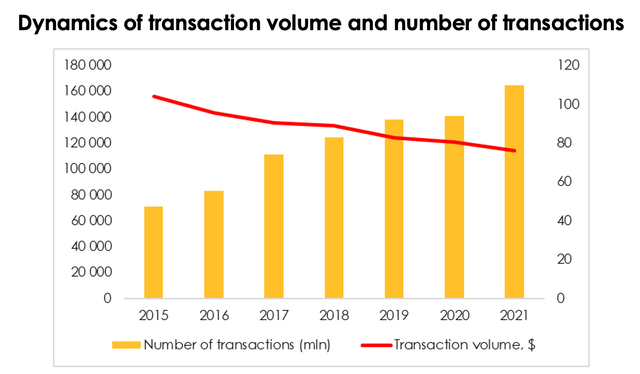
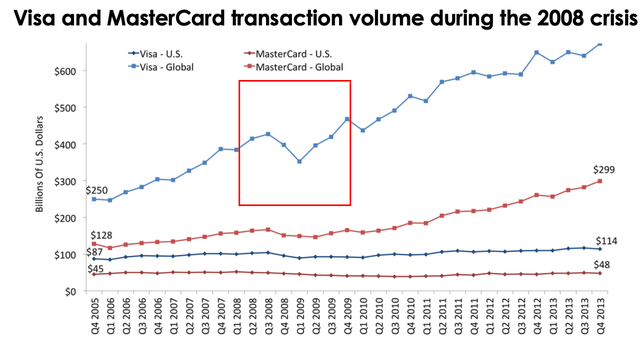
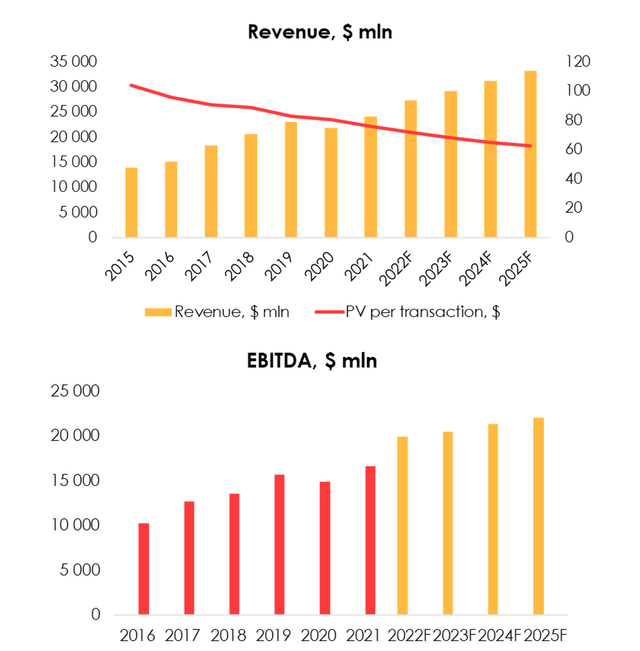
Credit cards have become a common tool for maintaining comfortable levels of consumption in the U.S. and worldwide, while debit cards have already replaced cash in many ways. The business of plastic card issuers has always demonstrated high stability of financial results. Between 2015 and 2021 revenue of Visa was increasing with an average growth rate of approx. 10%, while the average growth rate of transaction volume was 15%. The U.S. economic growth cycle we observed over the last 12 years after the 2008 crisis was favorable for the entire financial sector, including Visa.
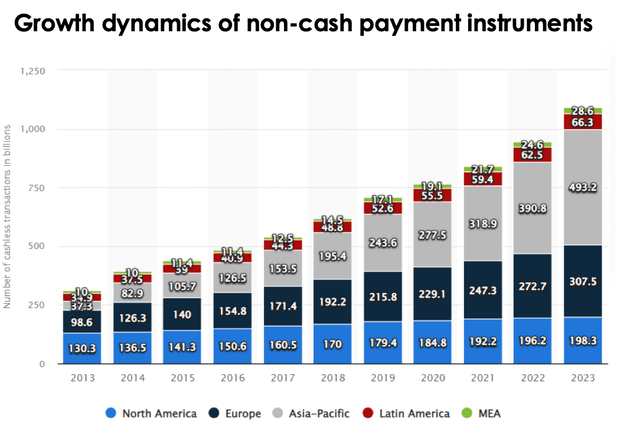
However, the success of Visa was largely due to the growing use of non-cash funds in payments. According to Statista, the volume of non-cash payments almost doubled between 2015 and 2021. The overall convenience of the system, the development of the e-commerce segment, automatic currency conversion and many other features of the service have significantly shifted consumer demand, as well as the desire of the population to use cash.
Nevertheless, BNPL (buy-now-pay-later) and POS (pay-on-sales) financing is rapidly growing and has all the chances to capture the market share of traditional payment systems, even though it has not yet taken such a significant place in the monetary system as bank cards.
The key point in the development of alternative sources of online payments is the emergence of the e-commerce market. In many ways, BNPL systems are more competitive as they offer lower rates (in some cases, the customer pays nothing for the loan), convenient integration into online shopping apps, and clear repayment schedule.
In addition, representatives of the alternative transaction business are significantly expanding their product range, turning their service into a full-fledged ecosystem. Specifically, Affirm (AFRM), Klarna (KLAR), Afterpay (OTCPK:AFTPF) and several other companies have developed shopping apps, and then there’s PayPal (PYPL), which issued virtual credit cards and acquired Honey – a coupon search service. The diverse development of services and large number of ways to boost consumer activity shall allow BNPL systems to increase their share of presence in the overall cycle of money conversion.
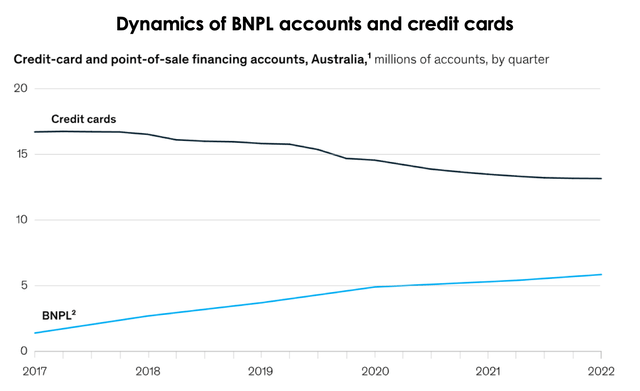
According to the recent McKinsey forecast, the development of alternative payment services may reduce the profit of credit card issuers in the U.S. by up to 15% in favor of new loan systems. The report also points out that in the market with advanced POS lending systems, such as Australia (can be used as a proxy for the U.S. economy), BNPL accounts were growing with an average rate of 40% per year over the past 5 years, while credit card accounts were declining by approx. 6% per year. While the agency notes that it expects a smoother effect in the U.S., its overall outlook of the consumer loan market is similar to the case of Australia.
Thus, despite the general trend towards the transition from cash to digital money, traditional cards have good reason to lose market share as new players evolve, so the long-term high revenue growth of the sector, including Visa, will be challenged by the headwind of competition. We don’t believe the effect will manifest itself immediately and the sector shall lose customers quickly, but the growth rate of the industry is likely to slow down in future.
Recession and the financial performance of Visa
The entire business of Visa is based on three inputs – the number of transactions, their size, and the level of monetization. Monetization level of Visa was always stable, ranging between 0.19 and 0.20%. Transaction volumes were increasing, while their average size was gradually decreasing due to more frequent use of plastic cards in everyday spending and substitution of cash.
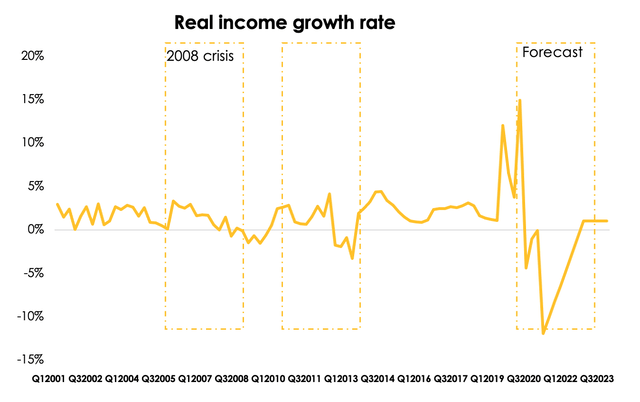
The growth of payments was provided not only by the shift of the economy to the digital zone but also by growing real income of the population. After the 2008 crisis, the U.S. economy entered the recovery cycle, largely driven by cheap borrowed funds.
During the 2020 crisis, zero interest rates only accelerated consumption, but the real income decline is inevitable due to the looming recession. On average, the real income tended to be stagnating or falling for about 7 months in a row during economic shocks. We expect similar dynamics in 2023 and believe that real income growth will have returned to its average of 1% only by early 2024. For example, according to the FRED, real income has already fallen by 12% y/y.
In the near term, the real income decline combined with increased competition may reduce the growth rate of Visa payment volumes or even reduce the indicator value in absolute terms. Such a situation took place in 2008, according to Insider.
On the other hand, the real income decline shall encourage the population to increase the amount of borrowing. However, we believe that this effect shall not be systematic.
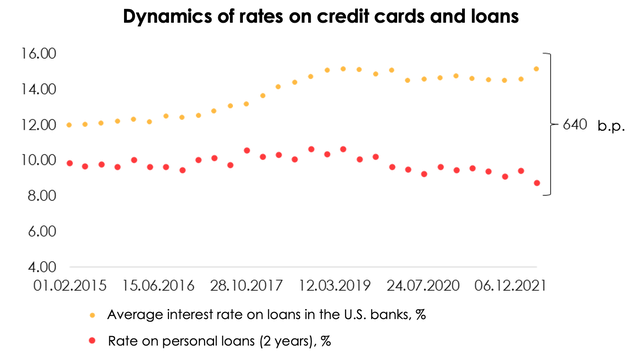
Firstly, credit card rates, according to the data, in the U.S. are significantly higher than rates on 2-year consumer loans, with the spread widening up to 640 bps over the last few months. It is much cheaper for a consumer to get a 2-year loan than to pay for a purchase by credit card.
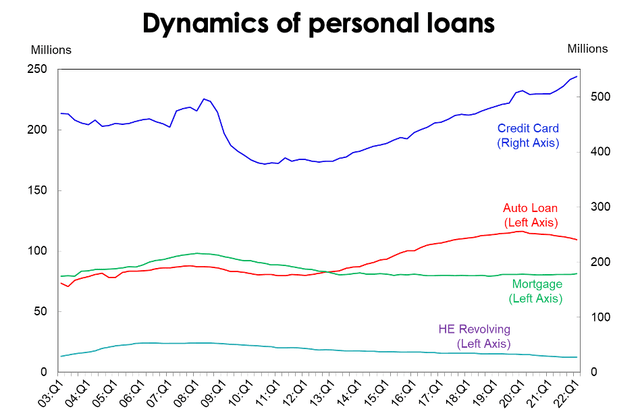
Secondly, the volume of open credit card accounts in the U.S. is at historically high levels, like in 2008. According to the New York Fed, their number is estimated at 537.11 mln with a total debt of $840 mln. Some accounts are included in the calculations twice because they are used by several people, but even if 30% of accounts are joint, the average American has 1.12 credit card accounts.
During periods of declining economic activity, consumers tend to reduce the amount of their borrowings, as they lose confidence in the economic growth and their future income. This was the case in 2008-2010, when the financial crisis resulted in many people abandoning their use of borrowed funds and the number of open credit card accounts declined by more than 20%.
We believe that the recession will have similar effect on the consumer loan market and the number of open accounts will drop as early as 2023. At the same time, credit card rates are likely to rise further with the key rate hike.
All good news is ahead
Although Visa will face problems in the medium term, we believe that the business remains attractive and patient investors can make good money on it.
If Visa fails to meet investor expectations due to lower operating results, the sell-off of the stock based on the report that could be worse than this year’s Q3-Q4 consensus (matching with Q4 22-Q1 23 for Visa) shall create attractive entry point for purchase.
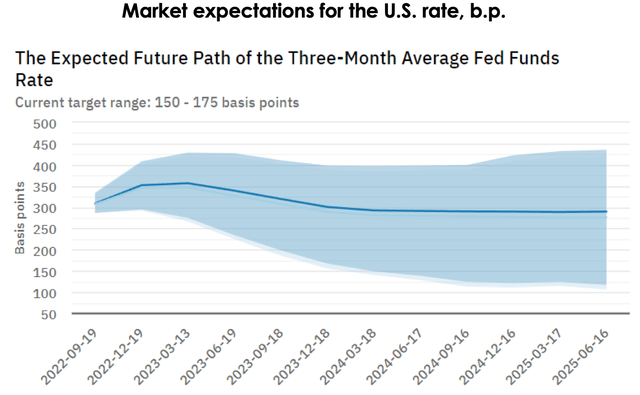
The market is already assuming the key rate reduction, according to Atlanta Fed, in the second half of 2023. The key rate reduction and liquidity injection shall increase the pace and volume of money movement in the commodity market by stimulating consumption and borrowing, so the base for Visa earnings will also expand significantly.
Valuation
According to our forecast and the company data, the revenue of Visa will grow at an average rate of about 8% over the next four years.
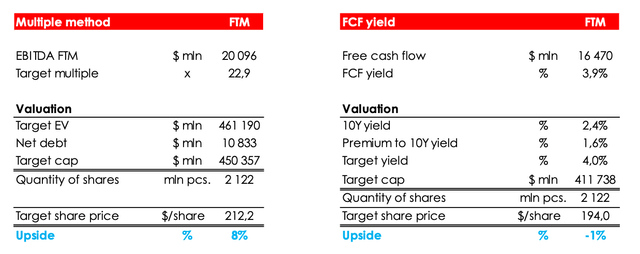
According to our valuation, the fair value of the stock price is $203.10 per share, so we consider the current market value to be fair and maintain a HOLD rating for the company. Upside – 0%.
The main drivers of the growth drivers of the stock are:
1) Continued worldwide transition from cash to non-cash transactions
2) Further Fed switch to dovish monetary policy and consecutive liquidity injection into the US economy
3) Possible collaborations with fintech industries resulting in a wider services list and Visa’s monetization opportunities
The main risk factors are:
1) A significant decrease in transaction volumes and credit card accounts during a recession
2) Intensifying competition in the transaction market resulting in consumer preferences shift from traditional transactions and credit methods to BNPL & POS services
Conclusion
Therefore, we see no reason to buy Visa in the portfolio right now. The market valuation of the company is still high, while competition in the digital payment market is growing, and the expected recession will hit the financial performance of Visa.
Nevertheless, we believe Visa is an outstanding mature business, and potential stock declines in the future could create an opportunity for attractive upside. Subsequent softening of the monetary policy could have positive impacts on the operating results of Visa, despite growing competition in the non-cash payment industry. We recommend keeping an eye on the company’s financial reports, national statistics (Fed, US Census Data) and the Fed’s agenda to effectively manage the entry point for the position.


Be the first to comment