TARIK KIZILKAYA/iStock Unreleased via Getty Images
Investment Thesis
Mastercard Incorporated (NYSE:MA) is one of the duopolies that dominates the global payment processing industry. This advantage allows it to benefit from economies of scale to secure a predictably increasing top and bottom line over the last 10 years. MA’s advantage is unlikely to be eroded by new players due to the high barriers to entry for smaller players. Even new digital wallets that were widely speculated to disrupt the dominance of incumbent players have largely chosen to leverage their market dominance instead of replacing them in the market.
Moving forward, MA has an effective “multi-rail strategy” to streamline the current different payment processes (or payment rails). Among the advantages of this strategy is the provision of Real-Time Payments (RTP). RTP alone is projected to have a total addressable market of $193.1 billion by 2030.
As one of the largest players in the payment industry, MA is able to accumulate a much larger volume of payment data compared to other smaller players. This means they have the ability to help customers “test run” their proposed payment solution using predictive analysis even before the solutions are implemented live. This is a service that other smaller players are unlikely to offer.
The stock is undervalued, which presents a great investment opportunity.
Company Overview
Mastercard was originally called “Interbank” and “Master Charge” back in the 1960s and 1970s. It was created to compete with BankAmericard (Currently VISA) issued by Bank of America. Since its inception, it has made numerous acquisitions and is now one of the largest payment processing companies in the world. Here are some notable examples:
Europay International – Before the acquisition, it was one of the most dominant credit card companies in Europe, together with VISA. Together with MasterCard and VISA, it forms the acronym of the more secure EMV payment technology, which is a global standard of authentication for payment transactions widely accepted around the world.
DataCash – This was a European payment service provider that is a global gateway for multi-channel payment processing.
Provus – This was a leading independent Turkish Payment Solutions Provider. It was the largest payment solution provider in Turkey.
These are the revenue streams of MasterCard, inferred from the company’s latest annual report 2021:
- Domestic assessment fees – These are “fees charged to issuers and acquirers based primarily on the dollar volume of activity on cards and other devices that carry the Company’s brands where the merchant country and the country of issuance are the same.”
- Cross-border assessment fees – These are essentially similar to ‘Domestic assessment fees’ in the previous point except that it includes currency conversion fees due to transactions being carried out across different currencies.
- Transaction processing fees – These fees are applicable for both domestic and international transactions. It pays for the switching services of authorization, clearing, and settlement of transactions. It also includes access to the company’s payment network by other financial institutions involved in the payment transaction process.
- Other revenues – These are fees for the provision of all other “miscellaneous” payment processing solutions.
Based on the latest Q1 2022 report, these are the “components of net revenue.”
Revenue Breakdown (latest Q1 2022)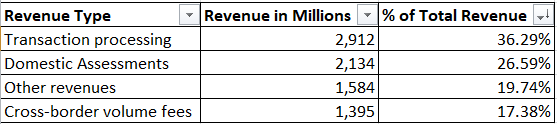
Although more than 60% of revenue comes from “Transaction processing” and “Domestic Assessments,” revenues from the other 2 components are “significant” and evenly distributed. As such, there is no concentration risk in the company’s revenue portfolio.
Economies of Scale and Barriers to Entry
The payment industry is largely dominated by 2 major players, namely, Visa and MasterCard, effectively forming a duopoly. This is in spite of the advent of digital wallets like PayPal and Block (formerly Square) which are functionally capable of bypassing the payment network of Visa and MasterCard altogether.
Due to this dominance, MA enjoys significant economies of scale. The barriers to entry are also high for new players to enter the market and challenge the incumbents directly. This is due to the extremely high costs associated with building the whole payment infrastructure from scratch. New players also need to gain the trust of financial institutions and cardholders to switch to a new relatively ‘unknown’ provider. In fact, among the smaller players in the industry, instead of seeing new entrants joining the market, a massive consolidation is taking place as I described in my previous article about Global Payments Inc (GPN).
There were speculations about competitors from Google Pay (GOOG, GOOGL), Apple Pay (AAPL), PayPal (PYPL), and other digital wallets disrupting the dominance of the current duopoly. However, as this article described, they have not been successful in doing so:
“Today most mobile wallet functions are tethered to a credit card or bank account, so there is little risk of them replacing credit cards in the current form,” said John Cabell, director of banking and payments at J.D. Power, a leading consumer intelligence firm. “And in fact, J.D. Power research shows that tethering a credit card to a mobile wallet increases satisfaction with the mobile experience.”
Due to the above reasons justifying the company’s economic moat, MA’s top and bottom lines have been on a clear uptrend for the last 10 years,
The effect of ‘Economies of Scale’ and ‘Barriers to Entry’ can be observed financially from MA’s top and bottom lines which have been on a clear uptrend for the last 10 years.
Top and Bottom Line Trend (Seeking Alpha)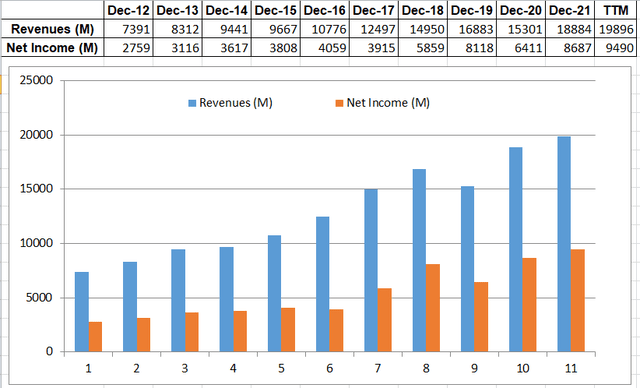
Multi-rail Strategy
MA already has a successful “Mastercard Track Business Payment Service” (MTBPS) that benefits the business community. According to this article:
Track Business Payment Service enables Buyers and Suppliers to manage their payments more efficiently – resulting in better outcomes for both parties. Suppliers can systemically manage how they get paid for different invoices for different Buyers. Buyers can optimize and automate efficiencies in paying Suppliers with improved reconciliation to manage cash flow and capture early payment discounts.
The ‘multi-rail strategy’, includes ‘Account-to-Account (A2A) payments functionality’ to allow A2A payments to enjoy the same streamlined payment processing provided by MTBPS. As explained in the article cited:
The new addition offers businesses a similar experience for A2A payments as they had with card payments. That is, businesses can exchange data with greater efficiency and facilitate payments across multiple payment rails including Real Time Payments (RTP) and the Automated Clearing House (ACH). Overall, the new tool enhances security, as it doesn’t require suppliers to share their bank account details with buyers, nor does it require buyers to store those details.
This is a great opportunity for MA to grow its revenue tremendously. As this article pointed out:
Global cashless payment volumes are set to increase by more than 80% from 2020 to 2025, from about 1 trillion transactions to almost 1.9 trillion, and to almost triple by 2030. Within the multi-rail payments ecosystem, RTP could reach $193.1 billion by 2030.
Use of Payment Data In Predictive Analysis
MA’s Test and Learn solution allows merchants to leverage MA’s massive consumer payment data to make predictive analyses. This feature helps merchants to determine how likely their planned initiatives are before committing real investment.
Not many payment companies can do this effectively. Accurate and meaningful predictions require a very large amount of payment data that spans many different payment scenarios. Right now, Visa (V) and Mastercard form the duopoly of the payment industry. In my opinion, this is one of the value-added services that smaller players will not be able to replicate.
Investment Risk
We are now experiencing a period of high inflation largely due to the pent-up consumer demand after the pandemic and the Russian invasion of Ukraine. As such, consumer spending could dip during a recession. This will hurt the revenue of all payment companies, not just MA.
In my opinion, other smaller industry players will be the hardest hit. Moreover, in spite of the pent-up demand during 2 years of the pandemic, some surveys also suggested consumer spending could still remain intact:
They’re venturing out of their homes again, but they’re continuing to spend money on home improvement. And—in what could be boon or bane for manufacturers and retailers—today’s consumers are quite willing to abandon their once-preferred brands in favor of new ones that offer value or novelty.
If MA’s profitability over the next few quarters does take a beating due to these macro headwinds, long-term investors should note that these are likely to be temporary and should be resolved in a multiyear horizon.
Valuation
We will calculate the intrinsic value of the company using the Discounted Free Cashflow model over a 20-year timeframe with the following assumptions and values:
- The last reported ‘Total Common Shares Outstanding‘ is 974.2M.
- The last reported ‘Total Cash & ST Investments‘ is 7,328M.
- The last reported ‘Total Debt‘ is 14,646M.
- The latest Free Cash Flow during the TTM period is 8,818M.
- The discount rate is estimated to be 8.25%, taken from the WACC value.
- The growth for the first 5 years is assumed to be 21.86% per year. This is inferred from ‘Free Cash Flow Per Share Growth Rate (FWD)‘.
- The growth for the next 5 years is assumed to be 15%, which is the average growth of the S&P 500 over the last decade (14.7%), rounded to a whole number.
- For the last 10 years, the company is assumed to grow at the ‘mean value’ of the U.S. GDP growth rate of 6.37%.
Intrinsic Value (Seeking Alpha and Other Sources Cited)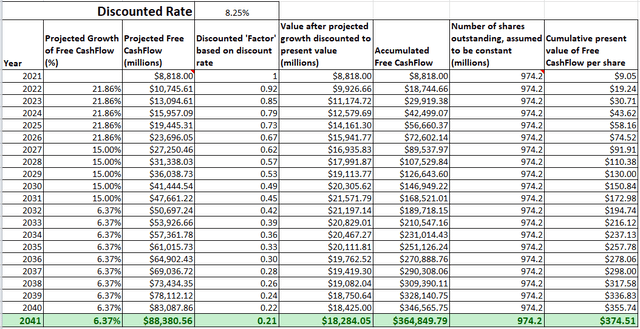
Based on the above inputs, the present value (“PV”) of projected Free Cash Flow per share for MA is $374.51.
Intrinsic Value (Seeking Alpha and Other Sources Cited)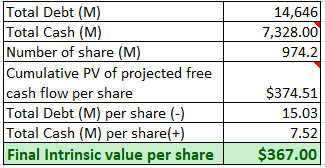
Taking into account the total debt and cash that the company is holding, the final intrinsic value is about $367, rounded off to the whole number.
MA’s share price is currently undervalued and selling at a discount of -12% ( 323/367-1).
Conclusion and Key Takeaway
As one of the largest players in the payment industry, MA has an economic moat that is strong and clearly observable, as discussed in earlier sections. In spite of its success in securing market dominance, the company is not sitting on its laurels. Its forwarding-looking growth plans suggested it is leveraging its advantages as a market leader to innovate and provide services that other smaller players are unlikely to provide.
The company is now undervalued, which presents a great investment opportunity for long-term investors.


Be the first to comment