wildpixel
Despite persistently high inflation, the decline in longer-term treasury bonds has stalled and investor appetite for riskier assets has begun to increase. Markets are weighing the potential benefits of lower interest rates versus the probability of recession. With relief from inflation on the horizon, whether economic activity normalizes with a soft landing or recession will determine asset prices going forward.
CPI Inflation
Headline CPI inflation continues to increase and is becoming broader based. This is not surprising, as the impact of higher energy prices are likely still feeding their way through the economy. It is probably concerning for the Fed though and may cause them to accelerate the tightening of monetary policy.
Figure 1: CPI Component Inflation by Percentile (source: Created by author using data from BLS)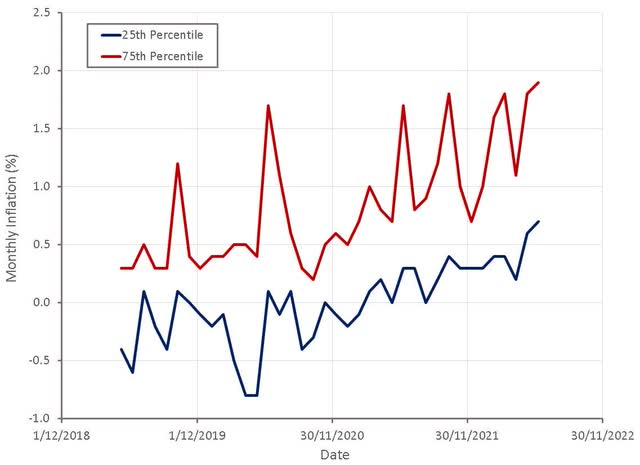
In contrast to headline inflation, YoY core CPI inflation has been declining modestly, primarily as a result of tough comparable periods in 2021. With easier comparable periods going forward, YoY core CPI inflation is likely to increase going forward.
Table 1: Core CPI Inflation (source: Created by author using data from BLS)
Despite concerns of a wage price spiral, and unanchored inflation expectations leading to higher inflation becoming embedded in the economy, inflation is likely to be resolved by a normalization of supply. Concerns over a wage price spiral have proven to be unfounded and it is growing increasingly likely that the cure for prices will be high prices, as demand is crushed. Consumer balance sheets may be strong but spending power is declining and there is a mounting negative wealth effect as asset prices drop.
Figure 2: Average Hourly Earnings Growth Minus Inflation (source: Created by author using data from The Federal Reserve)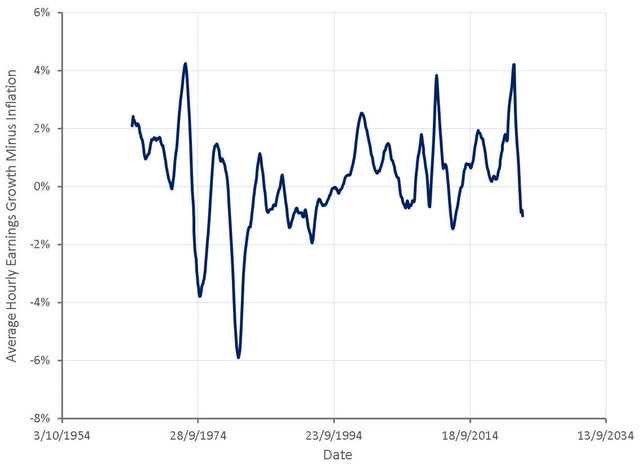
PPI Inflation
PPI inflation points towards a normalization of inflationary pressures, excluding the impact of supply issues. If commodity prices continue to trend downwards and economic growth stalls, it is possible that PPI inflation will be relatively low by the end of the year.
Figure 3: PPI Inflation (source: Created by author using data from BLS)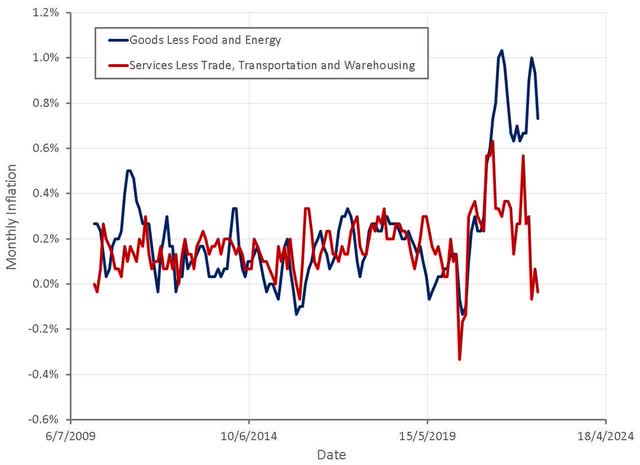
PPI inflation tends to lead CPI inflation and it would therefore not be unreasonable to expect CPI inflation to moderate later in the year as well. This will depend on how long demand remains robust and whether there are further supply shocks though.
Figure 4: PPI and CPI Inflation (source: Created by author using data from BLS)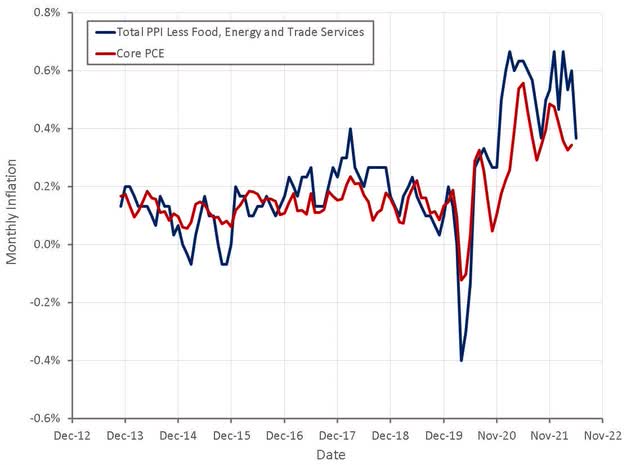
PPI inflation is likely moderating due to a combination of lower commodity prices and supply chain backlogs being worked though. The prices of many commodities are now down over 20% from their peak and manufacturing data indicates that the number of unfilled orders is in decline.
Figure 5: Current Unfilled Orders (diffusion index) (source: Created by author using data from The Federal Reserve)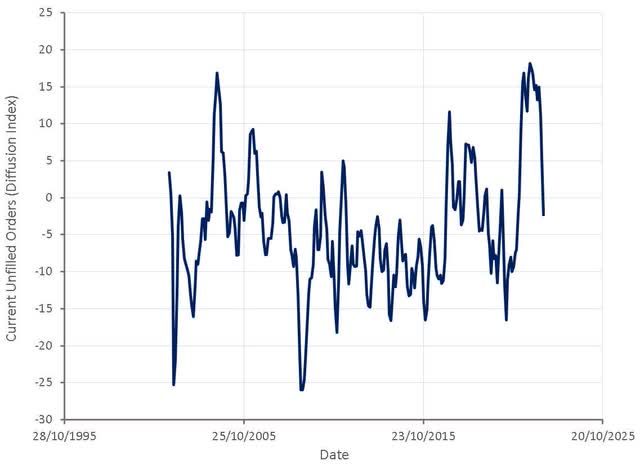
Data indicates that a resolution of supply chains issues and / or demand destruction is reducing inflationary pressure in a number of important areas:
Economic Conditions
Markets have largely shrugged off the CPI data, as focus has likely shifted to a broad range of leading economic indicators which are showing a rapid deterioration in conditions. Looking forward, manufacturers are growing increasingly negative about business conditions, with sentiment this negative generally associated with recessions.
Figure 6: Future General Business Conditions (Diffusion Index) (source: Created by author using data from The Federal Reserve)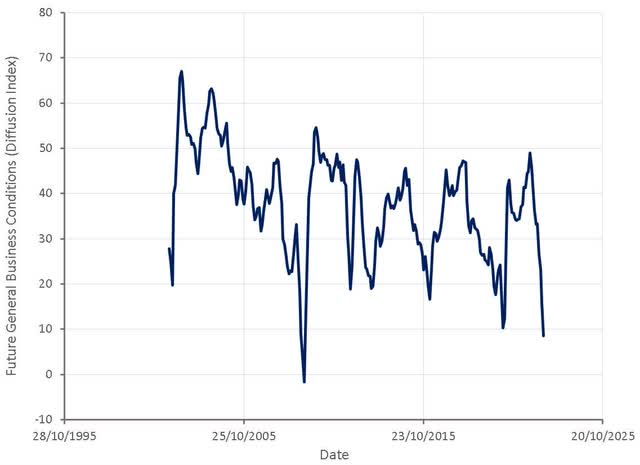
Housing market data indicates a rapid deterioration in conditions as the housing bubble begins to deflate. The NAHB housing market index shows weakness and the supply of housing on the market is beginning to normalize relative to demand.
The labor market remains relatively robust so far, which will allow the Fed to continue focusing on inflation. Employment is a lagging indicator though and by the time problems show up in labor markets a recession would likely be well under way.
Figure 7: Initial Claims (source: Created by author using data from The Federal Reserve)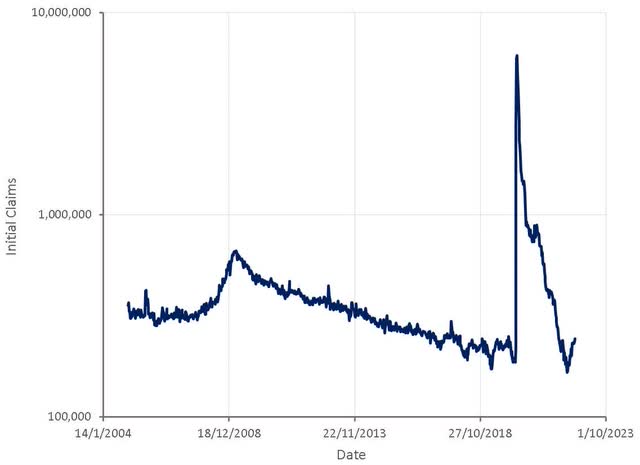
The yield curve slope is now firmly indicating a potential recession as the Fed hikes short-term rates and longer-term rates begin to reflect deteriorating economic conditions.
Figure 8: Yield Curve Slope (source: Created by author using data from The Federal Reserve)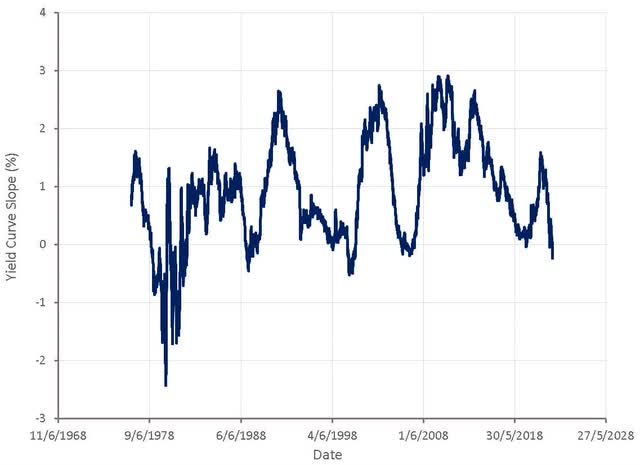
Conclusion
Deteriorating economic conditions are likely to negatively impact cyclical businesses. In particular, anything related to the housing market or durable goods is likely to face particular headwinds. Given the likelihood of lower long-term rates, investors may begin to seek more exposure to long-term bonds and high duration stocks, provided they are not overly sensitive to economic conditions.


Be the first to comment