
Drew Angerer/Getty Images News
Grizzly Research (“Grizzly”) has released a short-seller report on NIO (NYSE:NIO) Tuesday morning, citing the Chinese electric vehicle (“EV”) company has engaged in the exaggeration of revenue and profitability via aggressive accounting methods and fraudulent means. In addition to outlining the alleged measures NIO has taken to falsely inflate its top- and bottom-line since 2020, Grizzly has also gathered extensive research in an attempt to character-assassinate NIO CEO Bin Li in order to “dot the i’s and cross the t’s” in its argument that the three core elements of fraud – opportunity, incentive and rationalization – exist in this situation for the EV maker.
While some of the findings raised in the short-seller report may raise questions that only NIO management can answer, there are also questionable and groundless arguments made by Grizzly that could significantly mislead and deceive existing and potential investors in the EV stock. The following analysis will focus on an overview of the short-seller’s core claim against NIO – namely, false inflation of revenue and net income via aggressive accounting and potentially fraudulent means – and provide a walkthrough of questions / challenges we have over the validity of some of those claims.
Accounting Crash Course: NIO’s BaaS Revenue Recognition Method
Through publicly disclosed information within NIO’s audited annual report, Grizzly had identified that NIO is frontloading and inflating revenue recognition pertaining to its battery-as-a-service (“BaaS”) sales via an unconsolidated related party.
In 2020, NIO, alongside an external consortium of investors that consist of EV battery maker CATL, Hubei Science Technology Investment Group, and a subsidiary of Fuotai Junan International Holdings Limited, have together created the joint venture “Wuhan Weineng Battery Asset Co., Ltd.,” (“Weineng”). Weineng was established in 2020, the same time when NIO’s battery lending service BaaS was introduced.
Under BaaS, NIO customers are eligible for a one-time discount of up to RMB 128,000 ($19,133) on the vehicle purchase if they opt for the battery lending subscription program instead of buying the battery with the vehicle upfront. This strategy has been an effective mean in fuelling the adoption of NIO EVs in China, especially with additional government subsidies for purchases that are compatible with battery swapping technology. All sales and costs pertaining to BaaS are managed by Weineng.
Now, the Weineng joint venture, in which NIO holds a 19.8% equity interest in, has been accounted for as an “equity-accounted investment” on the EV maker’s financial statements, given the definition of control under GAAP-based accounting has not been met (further discussed in later sections). Under GAAP-based accounting for related party transactions, “intragroup related party transactions and outstanding balances are eliminated, except for those between an investment entity and its subsidiaries measured at fair value through profit or loss, in the preparation of consolidated financial statements of the group”:
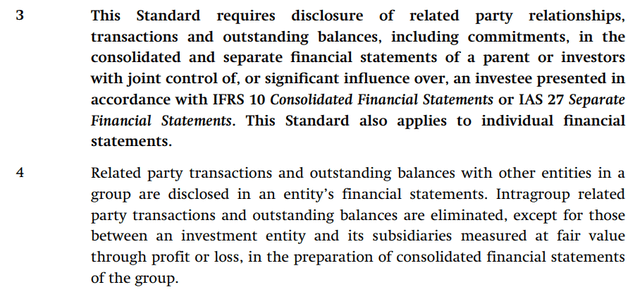
GAAP Rules on Related Party Disclosures (IAS)
Based on NIO’s disclosures within its audited annual report on its revenue recognition method pertaining to BaaS sales, the EV maker sells its battery packs to Weineng on a “back-to-back” basis when a vehicle is sold to a customer subscribed to BaaS:

NIO Revenue Recognition Policy on BaaS Sales (NIO 2021 20F)
In compliance with GAAP-based accounting for revenue recognition, a sale is reported to the income statement when a performance obligation is satisfied. Under NIO’s affiliation with Weineng, NIO sells Weineng a battery pack when a customer buys a vehicle with BaaS subscription. The performance obligation here is that NIO needs to provide a battery pack to Weineng, and once this is satisfied, NIO is permitted to recognize revenue on the battery sale based on a pre-contracted transaction price for the performance obligation. For NIO, the battery sold would have been previously considered as inventory. Following the recognition of the battery sale, NIO would have also recorded cost of sales pertaining to removing the battery from its inventory balance on the balance sheet:

Journal Entries for Battery Sales Business Model (Author)
In Weineng’s case, however, its performance obligation to customers is the provision of battery lending services on a monthly or annual basis, depending on the subscription option. As such, Weineng can only recognize monthly / annual BaaS revenue over time when it satisfies its battery lending obligation to customers. Weineng would also have to record depreciation costs over the useful life of its batteries, which are considered property, plant and equipment used in facilitating its service business:

Journal Entries for BaaS Business Model (Author)
This arrangement essentially allows NIO to recognize 100% of revenues pertaining to the battery pack sold to Weineng upfront upon selling a vehicle booked on BaaS on a one-for-one basis, instead of recognizing BaaS revenue and related depreciation costs on the batteries used in the BaaS business over time. The disclosed BaaS revenue recognition method for NIO also infers that the number of battery packs sold to Weineng should be equivalent to the number of BaaS subscribers as of period-end. BaaS revenues and related costs of sales (e.g. depreciation costs on batteries) recognized over time are instead in the books of Weineng, in which NIO accounts for on its balance sheet as an equity-accounted investment.
Because Weineng is an equity-accounted investment and not a consolidated entity in which NIO controls under the definition set out by GAAP-based accounting, NIO is not required to perform intragroup eliminations pertaining to the related party transaction. Instead, it is required to disclose the relationship, as well as the related amounts if material. This information is disclosed in NIO’s 2021 20F under “Note 26. Related Party Balances and Transactions”. Revenue and income generated by Weineng are accounted for in NIO’s financial statements as “share of (loss) / income of equity investees” pro-rated for its non-controlling interest.
Grizzly’s Core Short Thesis
Grizzly alleges the move is a fraudulent measure taken by NIO to “exaggerate revenue and profitability”. The short-seller has accused NIO of using the accounting “loophole” to frontload battery revenues pertaining to BaaS that should have been recognized over a course of about seven years (i.e. battery discount on BaaS vehicle purchase, divided by annual BaaS subscription fee).
In addition to frontloading revenue recognition on BaaS sales, Grizzly has also identified a discrepancy between the number of active BaaS subscribers and battery packs owned by Weineng as of September 30, 2021. Grizzly found that Weineng had ownership of 40,053 battery packs as of September 30, 2021, but only had 19,000 active BaaS subscribers during the period, which is inconsistent with NIO’s claims that it only records battery sales to Weineng on a back-to-back basis with BaaS vehicle sales. Grizzly has attributed the discrepancy as NIO’s way of artificially inflating revenues by selling more battery packs to Weineng than it needs to fulfil BaaS performance obligations.
In order to support its claim that NIO is defrauding investors via the unconsolidated related party, Grizzly has also gathered additional research in an attempt to support the three key elements of the fraudulent triangle:
Opportunity: As mentioned in the accounting overview section, the ownership structure between NIO and Weineng is accounted for as an equity-accounted investment, which allows NIO to bypass related party transaction eliminations on its financial statements. This accordingly provides an opportunity for NIO to artificially inflate its revenues at the group level by recording sales to the equity-accounted subsidiary, without the need to back it out at period end. Under GAAP-based accounting rules on related party transactions, NIO is required to disclose material details to the relationship, in which it has complied with.
The organizational structure also provides NIO an ability to recognize BaaS revenues upfront, instead of over an extended period of time given the difference in performance obligation it owes to Weineng compared to those Weineng owes to BaaS subscribers. Grizzly also claims the method has allowed NIO to bypass depreciation costs on battery assets to the tune of RMB 336 million per year.
Incentive: Grizzly has gone through extensive measures to dig up evidence to support NIO has a valid incentive for exaggerating its revenue and profitability. Citing an agreement between NIO and a state-backed consortium which has invested in a wholly-owned subsidiary “NIO China”, which requires NIO to redeem the investment upon failure in meeting pre-established performance metrics, such as achieving revenues of RMB 120 billion by 2024. However, the publicly disclosed information per NIO’s regulatory filings does not specify whether the RMB 120 billion revenue performance metric is required on an annual basis or on a cumulative basis between the time at which the agreement was forged with the state-backed investment consortium and 2024.
Grizzly has also inferred incentive for NIO to exaggerate its top- and bottom-line as a mean to pretty its valuation prospects, and attract investors from the public market.
Rationalization: The short-seller report lacks support for how NIO tried to rationalize the alleged fraudulent reporting behaviour. However, Grizzly has proceeded to gather evidence to bolster its claim of why the likelihood of fraud at NIO is high. These include findings about NIO CEO Li’s past association with personnel that have been previously linked to high-profile fraudulent financial reporting cases like Luckin Coffee (OTCPK:LKNCY). Grizzly has also alluded to questionable behaviour by NIO CEO Li, such as pledging a NIO-affiliated subsidiary, “NIO User Trust”, in which Li personally controls to UBS AG without directly addressing the matter to shareholders. While these findings may warrant clarification from management, there is insufficient ground to warrant a fraudulent sentence to the company.
NIO management has also refuted Grizzly’s claims, saying allegations outlined in the report are “without merit and contains numerous errors, unsupported speculations and misleading conclusions and interpretations”, and has committed to bolstering public disclosures going forward to protect shareholders’ interests. Nowhere has the company tried to outright rationalize fraudulent reporting.
Challenging Grizzly’s Conclusion on “Control” Established by NIO Over Weineng
In addition to character assassination on Li to support its claims for fraudulent reporting behaviour at NIO, Grizzly has also attempted to conclude NIO’s control over Weineng. As mentioned in earlier sections, if NIO effectively “controls” Weineng, it would have to consolidate the investment and eliminate any earnings recorded via related party transactions.
First, Grizzly has identified “conflicting disclosure” between NIO’s claim that it has “significant influence” over Weineng in one place, and NIO’s claim that it only has “limited control over the business operations” of Weineng in another place within a same regulatory filing. However, the words “significant influence” and “control” used within NIO’s regulatory filings are defined differently under GAAP-based accounting rules from general definitions of power that everyday investors are familiar with.
Significant influence is defined as “the power to participate in the financial and operating policy decisions of the investee without the power to control or jointly control those policies” under GAAP-based accounting. Significantly influence is typically established when an “entity holds, directly or indirectly, 20% or more of voting power of the investee”. NIO’s 19.8% equity interest in Weineng is sufficient to presume its “significant influence” over the investment:

GAAP Rules on Investments in Associates and Joint Ventures (IAS)
Pointing to our earlier reference to the definition of control established in GAAP-based accounting, the acquiring party only establishes “control” over the acquired party if it demonstrates three primary elements:
1. “Power” over the acquired entity, which is defined under GAAP as a substantive right exercised by an acquirer over the acquiree for non-protective benefits (e.g. exercising rights without the need for breach of contract or majority investor support). Based on publicly disclosed information in NIO’s regulatory filings, it only holds one of nine board seats on Weineng. There is also no mention of voting agreements that would pass on majority board and/or owner voting rights to NIO. With one of nine board seats, and a 19.8% equity interest, NIO does not exhibit power over Weineng to establish control.
2. Exposure to variable returns from the acquiree based on the acquirer’s involvement. NIO does not generate additional fees from Weineng based on Weineng’s performance. NIO is only exposed to Weineng’s earnings through its equity-accounted share of the investment.
As for the acquirer’s involvement in interfering with returns generated from the acquiree, Grizzly has pointed to the installation of two existing NIO executives to Weineng in management roles that include “Legal Representative and Chairman” and “General Manager and Director”. However, considering NIO’s significant influence over Weineng as defined under GAAP rules explained earlier, it is not unusual for the two parties to share employees or for NIO to “participate in the financial and operating policy decisions” of Weineng through the two shared employees. As such, NIO can account for its investment in Weineng as an equity-accounted investment, as long as “control” is not established even if it has installed employees at Weineng. Based on NIO’s failure to meet criterion 1 “power”, it already fails to establish control under GAAP rules over Weineng based on the existing ownership and voting structure disclosed in regulatory filings.
Grizzly has also alluded to the installation of two NIO executives in the daily operations of Weineng as a “major conflict of interest”. However, the auditor’s report per NIO’s audited 2021 20F states that “the company has maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2021, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the COSO”. The COSO framework requires that internal controls address segregation of duty requirements to ensure fair presentation of financial information without material misstatements whether due to error or fraud. As such, it is reasonable to believe that segregation of duty controls in place pertaining to the two executives’ roles in both NIO and Weineng have been tested as effective as of the reporting date.
3. The acquiring party is a principal in the transaction, and not an agent. Under GAAP-based accounting, an agent is “primarily engaged to act on behalf and for the benefit of another party…[and] does not control an investee when it exercises decision-making rights delegated to it”. In determining whether NIO is an agent over Weineng, the i) scope of NIO’s decision-making authority over Weineng, ii) the rights held by other investors in Weineng, iii) the remuneration in which NIO is entitled to in its affiliation with Weineng, and iv) NIO’s exposure to variability of returns from its interest in Weineng must be considered:
- Based on the foregoing analysis, we know that NIO’s sole decision-making authority over Weineng is limited given it only holds 19.8% equity interest with one in nine board seats in the joint venture. The two NIO executives installed in the daily operations of Weineng also do not exhibit characteristics of sole control over the joint ventures’ business.
- The remainder of the investment consortium over Weineng holds the remaining eight of nine board seats, and 80.2% equity interest in the joint venture. There have also been no mention of signed-over voting rights by the investment consortium to NIO in publicly disclosed information that would give NIO control over Weineng.
- In addition to battery sales, NIO is also entitled to service revenue earned from Weineng through service agreements. NIO earns revenue for providing “battery pack monitoring, maintenance, upgrade, replacement, IT system support, etc.” to Weineng via monthly service charges. As of the reporting year ended December 31, 2021, service revenues pertaining to the service agreements between NIO and Weineng were immaterial according to disclosures in “Note 2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies”, section (r) Revenue recognition in the 2021 20F.
- As discussed in the control assessment under criterion 2, NIO’s exposure to variability of returns in its investment in Weineng is insufficient to establish control under GAAP-based accounting.
Challenging Grizzly’s Quantification of NIO’s Alleged Revenue and Profit Inflation
Grizzly believes NIO has inflated revenue and net income by “about 10% and 95%, respectively”, via its affiliation with Weineng. Grizzly’s calculations, as well as our skepticism, is outlined as follows:
1. Frontloaded Revenue via Battery Sales to Weineng
Grizzly’s accusation. As discussed in the foregoing analysis, Grizzly identified that NIO has been recognizing battery revenues pertaining to BaaS upfront via its affiliation with Weineng. Instead of recognizing BaaS revenues over time when the service performance obligation is satisfied, NIO is able to recognize 100% of battery revenues sold to customers via BaaS subscriptions through the Weineng JV. Grizzly claims that this arrangement effectively allows NIO to pull forward seven years of BaaS revenue upfront.
Grizzly’s calculation of quantified impacts. Considering vehicle purchase discounts ranging RMB 70,000 (70/75 kWh battery pack) to RMB 128,000 (100 kWh battery pack) upon buyer’s subscription to BaaS, Grizzly has taken the lower end of the range (i.e. RMB 70,000) as the proxy for battery pack revenues. Based on annual BaaS subscription fees at RMB 11,760 (RMB 980/mo.) for the 70 kWh battery pack, which yields a vehicle discount of RMB 70,000 with subscription to BaaS, Grizzly has assumed a BaaS revenue recognition timeline of about seven years (i.e. RMB 70,000 discount, divided by RMB 11,760 annual BaaS subscription fee, adjusted for inflation) – we consider this a reasonable assumption.
Now, as of September 30, 2021, a public regulatory filing by Weineng disclosed that it had 19,000 active BaaS subscribers. 18% of its subscription base were subscribed to the RMB 1,480/mo. 100 kWh battery pack, and 82% were subscribed to the RMB 980/mo. 70/75 kWh battery pack at the time.
Grizzly’s calculation of inflated revenues and income pertaining to NIO’s sale of 19,000 BaaS-related batteries to Weineng in the nine months ending September 30, 2021 is as follows:

Grizzly’s Computation of Inflated Revenue and Income Pertaining to Pulled Forward BaaS Sales (Grizzly Research)
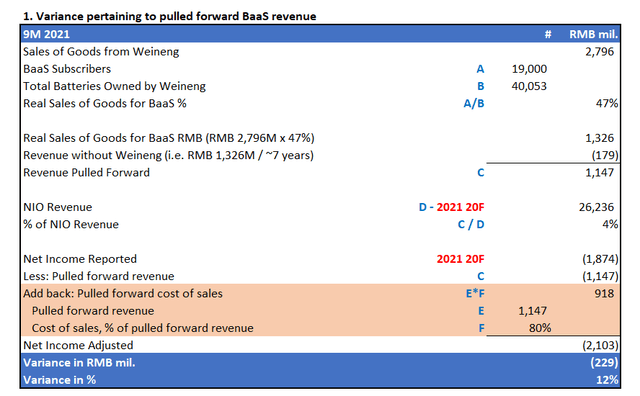
As of the nine months ended September 30, 2021, NIO had generated RMB 2,796 million in revenues from the sale of batteries to Weineng (full year 2021 revenues generated from Weineng: RMB 4,138 million, 11% of total NIO 2021 revenue). Based on 19,000 active BaaS subscribers, and ownership of 40,053 battery packs owned as reported by Weineng as of September 30, 2021, Grizzly estimates that only 47% of the RMB 2,796 million in revenues generated from the sale of goods to Weineng are related to “real” BaaS sales. Essentially, Grizzly claims only RMB 1,326 million of RMB 2,796 million in sales of goods to Weineng recognized on NIO’s income statement in the nine months ended September 30, 2021 are related to real BaaS battery sales.
The RMB 1,326 million pertaining to 19,000 battery packs sold to Weineng for the number of active BaaS subscribers at the time is effectively the “upfront” revenue recognized by NIO, which should have been recognized over a course of seven years instead based on the estimated performance obligation timeline discussed in earlier sections. Without Weineng, NIO would have instead had to recognize BaaS revenues related to the 19,000 subscribers over time, which is equivalent to RMB 179 million in the nine month period ending September 30, 2021. This essentially means NIO had allegedly pulled forward RMB 1,147 million in revenues related to BaaS sales in the nine months ending September 30, 2021.
In the nine months ended September 30, 2021, NIO had reported total revenue of RMB 26,236 million and net losses of RMB 1,874 million. The RMB 1,147 million in pulled forward BaaS revenues represents 4% of total revenues recognized over the nine-month reporting period.
To generate the “adjusted” net income that NIO would have reported had Weineng never existed, Grizzly had removed RMB 1,147 million in pulled forward revenues pertaining to BaaS sales directly from actual reported net losses of RMB 1,874 million. This accordingly yields adjusted net losses of RMB 3,021 million for the nine months ending September 30, 2021 at NIO, or a variance of 61%.
Issue with Grizzly’s claim. In Grizzly’s calculation of adjusted net losses had BaaS revenue never been pulled forward at NIO via its affiliation with Weineng, the short-seller did not add back costs of sales that NIO would have recognized when it sold the battery packs to Weineng and recorded the related revenue.
While profit margins on NIO’s battery pack sales to Weineng are not disclosed, Grizzly had used 20% as a proxy, which is “consistent with the margin of an entire vehicle [considering] batteries are a cost center for all vehicles”. Using the 20% profit margin proxy on 19,000 battery pack sales to Weineng totalling RMB 1,326 million in the nine months ending September 30, 2021, NIO would have recorded related cost of sales of RMB 1,060.9 million (i.e. 0.8% cost of revenues x RMB 1,326 million battery revenues recorded on the sale of 19,000 units to Weineng in the nine months ending September 30, 2021).
When Grizzly removed/pulled forward BaaS revenues of RMB 1,147 million from NIO’s actual net losses of RMB 1,874 million reported in the nine months ending September 30, 2021, Grizzly should have also added back related cost of sales totalling RMB 917.6 million in determining the adjusted net income reported.
Livy’s revised calculation of quantified impacts.
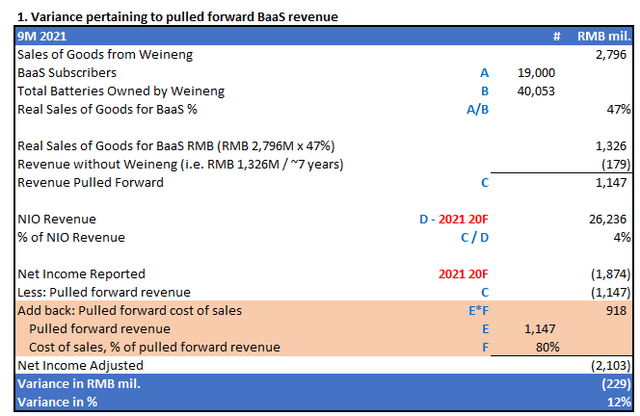
Livy’s Computation of Revenue and Income Variances Pertaining to NIO’s Alleged Frontloading of BaaS Sales (Author)
The above revised net income adjustment backs out alleged pulled forward BaaS revenues by NIO through its affiliation with Weineng from actual net losses reported by NIO in the nine months ending September 30, 2021. The orange-highlighted cells represent the incremental cost of sales pertaining to pulled forward BaaS revenues that should have been added back to adjusted net income in order to represent a fair representation of NIO’s adjusted net losses for the nine months ending September 30, 2021 if Weineng never existed and the EV maker had to recognize BaaS revenues over time. This adjustment accordingly reduces the variance of 61% from Grizzly’s calculation of adjusted net losses, to 12% – a material difference that, like Grizzly is accusing NIO of doing, misleads investors on the matter discussed.
2. Revenues from Oversupplied Batteries to Weineng
Grizzly’s accusation. Based on NIO’s revenue recognition method on BaaS sales, the number of battery packs sold to Weineng should be equivalent to the number of vehicle buyers that have subscribed to BaaS at the time of purchase. Based on 19,000 active BaaS subscribers reported by Weineng as of September 30, 2021, it is easy to assume that NIO should have only sold 19,000 battery packs to Weineng in the nine months ending September 30, 2021 as well to comply with the EV maker’s revenue recognition method on BaaS sales outlined in its 2021 20F.
However, Weineng had reported ownership of 40,053 battery packs as of September 30, 2021, which exceeds its active subscriber base of 19,000 by 21,053 units. As such, Grizzly has accused NIO of intentionally overselling battery packs to Weineng to inflate revenues.
While the discrepancy is indeed a question for management, Grizzly had cited that there is no need for Weineng to hold that many additional battery packs, even for operational purposes. Grizzly had gone on to explain its field work done at NIO Power Swap stations to verify that there is no difference between BaaS battery packs owned by Weineng and battery packs used in swap stations owned by NIO. However, we believe the additional field work is a moot point, considering NIO Power Swap operations are not related to Weineng. Weineng only facilitates NIO’s BaaS battery lending business, and nothing else – Grizzly did not even have to go out of its way to check on NIO’s Power Swap stations and hold conversations with sales staff at NIO’s car centers.
Livy’s response. While the number of battery packs owned by Weineng should essentially be equivalent to the number of active BaaS subscribers, there is a possibility that a total of 40,053 NIO vehicle sales between 2020 when BaaS was established and September 30, 2021 had subscribed to BaaS. Perhaps, as of reporting date on September 30, 2021, there were 21,053 BaaS subscribers that have halted monthly subscriptions, which is not surprising given the third quarter is not a typical driving season, and there is a possibility that these NIO vehicle owners did not need to use their vehicles during the period.
Grizzly has also supported its claim that NIO oversupplied battery packs to Weineng to intentionally inflate revenues by saying that Weineng has no storage facility to store its 21,053 excess battery packs as of September 30, 2021. However, we do not find this surprising, as BaaS subscribers that have halted monthly subscriptions might be holding onto the emptied battery packs on consignment or have returned them to a NIO servicing center where NIO has held onto these Weineng-owned battery packs on consignment. The lack of battery pack storage facility owned by Weineng does not conclude that its ownership of the excess battery packs is fraudulent and made up.
There can be many reasons why a discrepancy exists between the number of active BaaS subscribers and battery packs owned by Weineng at the end of a reporting period. The above are just two assumptions that could invalidate Grizzly’s accusation (which is also an assumption). The real answer to the discrepancy can only be explained by NIO and Weineng management.
Grizzly’s calculation of quantified impacts. In determining the inflated revenue and earnings specific to the allegedly oversupplied battery packs from NIO to Weineng, Grizzly had performed the following calculations:
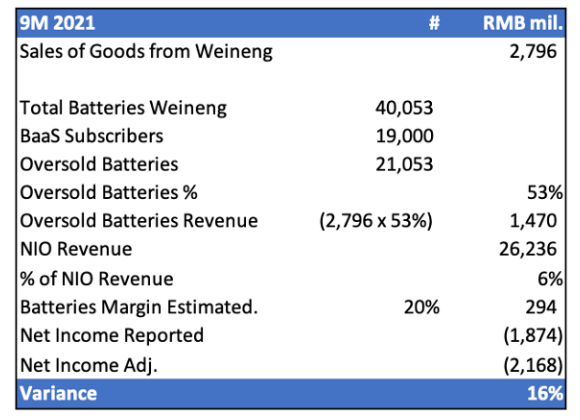
Grizzly’s Computation of Revenue and Net Income Variances Pertaining to Oversupplied Batteries (Grizzly Research)
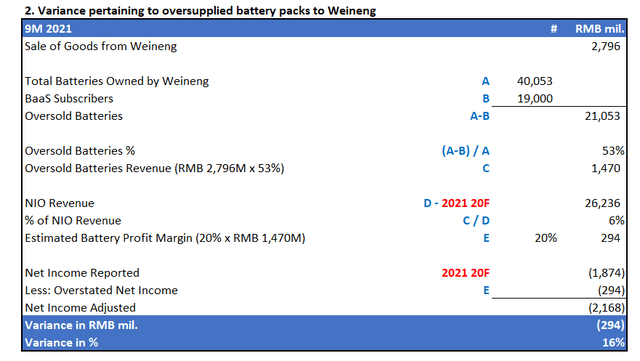
In deriving the inflated revenues related to the allegedly oversupplied battery packs, Grizzly had determined the percentage of battery packs owned by Weineng as of September 30, 2021 that were in excess to its active subscriber base as 53% (i.e. 21,053 excess battery packs, divided by 40,053 battery packs owned by Weineng as of September 30, 2021). The percentage was applied to total revenue recognized by NIO pertaining to the sale of battery packs to Weineng in the nine months ending September 30, 2021, resulting in oversold battery revenues of RMB 1,470 million (i.e. 53% oversold batteries x RMB 2,796 million in related party revenues from Weineng recorded by NIO for the nine months ending September 30, 2021).
In the nine months ended September 30, 2021, NIO had reported total revenue of RMB 26,236 million and net losses of RMB 1,874 million. The RMB 1,470 million in oversold battery revenue represents 6% of total NIO revenues recognized over the nine-month reporting period.
Considering Grizzly’s 20% profit margin assumption on battery pack sales as discussed in earlier sections, the oversold battery packs to Weineng would have generated net income of RMB 294 million in the nine months ending September 30, 2021. As such, backing out RMB 294 million in overstated profits back to NIO’s actual reported net losses of RMB 1,874 million in the nine-month period ending September 30, 2021 would have yield adjusted net losses of RMB 2,168 million, representing a variance of 16%.
We have no issues with this calculation performed by Grizzly, other than concerns over the short-seller’s claims that these 20,053 battery packs were intentionally “oversold” by NIO to Weineng to artificially boost revenues.
3. Shifting Depreciation Costs
Grizzly’s Accusations. Grizzly has accused NIO of indirectly shifting depreciation costs on the battery packs sold to Weineng, saving the EV maker north of RMB 336 million in depreciation expense on an annual basis.
Specifically, Grizzly has assumed a 20% profit margin on NIO’s battery sales totalling RMB 2,796 million generated from Weineng in the nine months ending September 30, 2021. This represents battery assets valued at a cost basis of RMB 2.25 billion (i.e. 80% cost x RMB 2,796 in battery sales to Weineng, adjusted for minor rounding differences) removed from the EV maker’s balance sheet over the same period.
Based on the five to eight years useful life attributable to equipment, including battery packs, used in NIO’s Power Swap business as disclosed in its 2021 20F, Grizzly has assumed an annual depreciation rate of about 15% on the battery packs sold to Weineng and removed from NIO’s balance sheet in the nine months ending September 30, 2021. This is consistent with the assumed BaaS revenue recognition timeline of about seven years as discussed in earlier sections. As such, Grizzly has accused NIO of avoiding depreciation costs of RMB 336 million (i.e. 15% battery depreciation rate x RMB 2,796 million in battery pack sales to Weineng) in the nine months ending September 30, 2021. The short-seller has also alluded to the RMB 336 million as a proxy for annual depreciation costs that NIO has avoided via its arrangement with Weineng.
Issue with Grizzly’s claim. There are two folds to this situation:
1. BaaS Business Model: Under the BaaS business model, the battery packs are considered equipment used in facilitating a service business. As such, the related battery packs would be subjected to depreciation over its useful life. In NIO’s case, if Weineng never existed and the EV maker consolidates its BaaS business, NIO would have had to recognized BaaS revenues pertaining to the 19,000 battery packs that Grizzly has attributed to the BaaS business over seven years, and accordingly record depreciation costs on these battery packs as well over their useful lives of about seven years. As mentioned in earlier sections, the related journal entries under the BaaS business model is as follows:

Journal Entries for BaaS Business Model (Author)
2. Battery Sales Business Model: in the current situation where NIO has sold the battery packs to Weineng, the battery packs are considered inventory to NIO. There is no depreciation costs related to inventory under GAAP-based accounting. Instead, NIO needs to record the costs of this inventory when they are removed from its balance sheet once the sale is recognized. As mentioned in earlier sections, the related journal entries under the battery sale business model is as follows:

Journal Entries for Battery Sales Business Model (Author)
Now, in NIO’s current actual situation, it is engaged in a battery sales business model under its performance obligation to Weineng, while Weineng is engaged in a BaaS business model under its performance obligation to BaaS subscribers.
As discussed in our first challenge to Grizzly’s calculations pertaining to pulled forward revenue on BaaS battery sales to Weineng, NIO would have recorded costs of sales pertaining to the sold battery inventory when it recognized the related revenues. And this cost of sales number, based on a 20% profit margin assumption consistent with that used by Grizzly, would have accounted for the costs of battery inventory removed from NIO’s balance sheet upon completion of the sale to Weineng. This is consistent with Grizzly’s own calculation pertaining to profit margins on the battery packs that it alleges NIO had oversupplied to Weineng, which is inclusive of cost of sales related to written off inventory incurred by NIO upon recognition of related revenues.
If NIO was engaged in the BaaS business model itself, without the intervention of Weineng, it would have recognized depreciation at a rate of 15% per year on the battery packs. However, under the upfront sale of related battery packs to Weineng, NIO would have recorded related cost of sales at an upfront rate of 80% as well. So basically, instead of recording revenues and depreciation costs on battery packs over time, NIO essentially recorded revenues and battery inventory costs upfront under its current arrangement with Weineng.
Grizzly’s calculation of quantified impacts. Grizzly’s accusation that NIO has overstated revenues and earnings by 10% and 95%, respectively, through its affiliation with Weineng is calculated as follows:
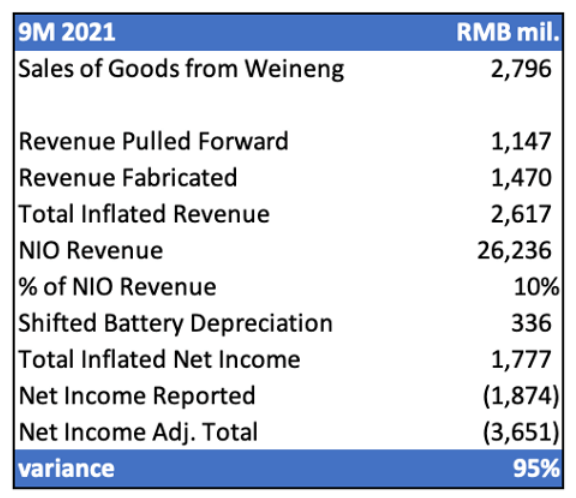
Grizzly’s Computation of Total Revenue and Income Inflation (Grizzly Research)
As discussed in earlier sections, NIO’s pulled forward BaaS revenues and inflated battery sales revenues via its affiliation with Weineng represent 4% and 6% of its total revenues, respectively, recognized in the nine months ending September 30, 2021. This represents the 10% in inflated NIO revenues as Grizzly has outlined in the above calculation.
Livy’s revised calculation of quantified impacts. While we have yet to reconcile the RMB 1,777 million in total inflated net income that Grizzly has accused NIO of recognizing (please let us know in comments if you know), we believe the 95% variance identified by Grizzly is not a fair presentation of the quantified impact of its core short thesis.
Our calculation of the quantified impact pertaining to Grizzly’s accusations that NIO has inflated revenue and earnings through (1) pulling forward BaaS sales, and (2) oversupplying batteries to Weineng, is as follows:
Livy’s Computation of Alleged Overstatements Related to Alleged Frontloading of BaaS Revenue (Author)
Livy’s Computation of Alleged Overstatements Pertaining to Alleged Overselling of Battery Supplies (Author)

Livy’s Computation of Alleged Revenue Overstatement (Author)

Livy’s Computation of Alleged Overstatement in Net Income (Author)
Under Grizzly’s accusations of inflated revenue and earnings by NIO through its affiliation with Weineng, if found valid (which we remain skeptical of), NIO would have overstated net losses in the nine months ending September 30, 2021 by 28% instead of the 95% that Grizzly alleges – a material difference that again misleads investors on the estimated quantified impact pertaining to the accusations claimed by the short-seller. The net income variance of RMB 523 million ($78 million) found in our calculation is also immaterial (< 1%) based on NIO’s market value of $58.38 billion as of September 30, 2021 and NIO’s market value of approximately $35 billion today.
Final Thoughts
As discussed in the introduction of this analysis, Grizzly had also touched on things like NIO CEO Li’s association with fraudulent personnel, the pledge of NIO User Trust to UBS AG, and conflict of interests to further support its argument that NIO is engaged in fraudulent financial reporting. However, these are groundless allegations that have yet to be substantiated to infer Li is committing fraud via NIO’s operations. While investors should always exercise professional skepticism on publicly disclosed information in regulatory filings when making investment decisions, the same skepticism should also be placed on external claims – such as those by the short-seller, commentary by external sources, and/or even commentary herein – especially if they argue that correlation = causation (e.g. Grizzly’s method in inferring that fraud at NIO is substantiated given “dirt” it has dug up on Li’s past).
While we agree that there are some good takeaways from the short-seller report that may require further clarification from management, it is important to recognize and acknowledge that a lot of it might also be misleading – or in the words of Grizzly, “exaggerated”. This is also consistent with NIO’s stock performance during Tuesday and Wednesday’s session following release of the short-seller report. The stock has largely moved in consistency with the ongoing market rout, and broad-based selloff across the EV sector, with no extreme deviation due to the negative headline from Grizzly, which indicates that market participants, especially significant shareholders in NIO, are still digesting the latest external allegations.
At the end of the day, NIO remains one of the most viable EV businesses in the emerging sector, with continued demand for its vehicles to support further growth over the long-run. Unlike some of the upstarts in the increasingly competitive EV landscape that have been accused of fraud, such as Nikola (NKLA), Lordstown Motors (RIDE), and Faraday Future (FFIE), NIO already operates a global business with a substantiated vehicle order book to support the bulk of its top- and bottom-line expansion, which continues to support its positive valuation prospects ahead.


Be the first to comment