4kodiak/iStock Unreleased via Getty Images
Amazon’s (NASDAQ:AMZN) position on top of the e-commerce industry is underpinned by its self-reinforcing network effect from Amazon Prime. For over a decade, Amazon has been consistently advancing the appeal of the Prime subscription service, attracting both buyers and sellers to the platform. In 2022, Amazon has strived to expand the Prime network effect beyond Amazon.com through the introduction of ‘Buy with Prime’, while seeking to maintain the appeal of listing on the Amazon marketplace.
Amazon Prime
Launched in 2005, Amazon Prime is one of the most successful digital subscription services, boasting around 200 million subscribers (2021 figure). It started off as offering free and fast shipping for certain products sold on the Amazon marketplace, and has evolved into offering many additional benefits, including Prime Video, Prime Music, free two-hour grocery delivery and more. Persistent enhancements in membership perks have made the subscription service increasingly sticky over the years, conducive to subscription growth and high membership renewal rates.
A growing base of loyal customers induces recurring visits to the Amazon marketplace and higher conversion rates for Amazon as paying subscribers are more likely to purchase products on Amazon.com than elsewhere in order to extract more value out of their subscription service. As a result, the growing Prime subscription base helps attract more and more sellers to the platform, and join the Seller Fulfilled Prime program to gain access to this loyal base of shoppers. More sellers joining the Prime network means more products available for fast and free delivery, in turn further augmenting the appeal of Prime membership to encourage more shoppers to join. Thereby, the e-commerce giant has successfully built a self-reinforcing network effect around Amazon Prime.
Amazon Prime has essentially set the industry standard for customer service, and has raised the bar for shipping and delivery services. Amazon has competently built out a fulfilment network over the last 25 years that enables the company to facilitate one-day and same-day delivery, and is a key attribute of Amazon’s moat to fend off rising e-commerce rivals. Amazon Prime has lifted customer expectations of delivery speeds, forcing competitors to play catch up.
Amazon sellers that want to join the Amazon Prime Network are obliged to meet targets for fast delivery promises through the use of Amazon’s Seller Fulfilled Prime carriers. Furthermore, Prime sellers must also comply with the Amazon Returns Policy and allow Amazon to deal with all customer service inquiries on their behalf. This allows Amazon to remain in control of the customer experience and thereby mitigate the risk of third-party sellers’ failures diminishing the appeal of the Amazon prime membership. Sellers are required to play by Amazon’s rules to benefit from its loyal Prime membership base.
Does ‘Buy with Prime’ undermine the need to sell on Amazon marketplace?
As the e-commerce industry has continued to evolve, it has given rise to new competitors like Shopify (SHOP), that help D2C merchants set up and run their own e-commerce websites, as opposed to listing on the Amazon marketplace. Shopify has witnessed a tremendous growth in its merchant-base over the years, posing a competitive threat to Amazon.
In April 2022, Amazon introduced ‘Buy with Prime’, which enables external D2C merchants to use Amazon’s Prime fulfillment services and grants them access to the e-commerce giant’s loyal Prime members. Moreover, the program enables digital merchants to place ‘Buy with Prime’ badges next to the products listed on their websites. It allows Prime members to check out using their Amazon account on brand websites outside of Amazon.com. ‘Buy with Prime’ is sold to digital merchants as a way to improve sales conversions, capitalizing on Amazon’s brand reputation of fast and reliable delivery.
The introduction of ‘Buy with Prime’ essentially eliminates the need to list products on the Amazon marketplace and join the Seller Fulfilled Prime program to benefit from industry-leading fulfillment capabilities and access loyal Prime members. Running their own websites, while continuing to benefit from Prime benefits through ‘Buy with Prime’, would enable merchants to stay in control of the customer experience and build their brand image, without being restricted by Amazon marketplace/ Prime program rules.
As a result, ‘Buy with Prime’ could discourage certain merchants from listing on the Amazon marketplace to escape the intensely competitive environment, and run their own websites instead to augment brand differentiation efforts, to the benefit of e-commerce web developers like Shopify and BigCommerce. Fewer merchants listing their products on the Amazon marketplace could diminish the on-site network effect, as it may subdue the recurrence of web visitors, thereby undermining both product sales and advertising revenue.
That being said, Amazon has wisely expanded Prime membership benefits beyond offering fast and free delivery to shoppers. Hence, Prime members have various other reasons to visit Amazon.com, including streaming entertainment on Prime Video, as well as regular grocery shopping, which can be well-imbedded into members’ routine habits. Furthermore, the ability to shop on various brands’ websites outside of Amazon indeed augments the appeal of Prime membership. Therefore, while ‘Buy with Prime’ may discourage listings on the Amazon marketplace among certain merchants, it will certainly not undermine consumers’ willingness to become Prime members/ renew Prime subscriptions.
Furthermore, ‘Buy with Prime’ grants Amazon access to e-commerce activity data from external websites, which could feed into augmenting Amazon’s targeted advertising solutions, and thereby improving Amazon advertisers’ sales conversion rates. Given the benefits the Amazon platform continues to offer, merchants are more likely to maintain dual listings (on Amazon and elsewhere), as opposed to completely de-listing from Amazon altogether.
Counteractive considerations
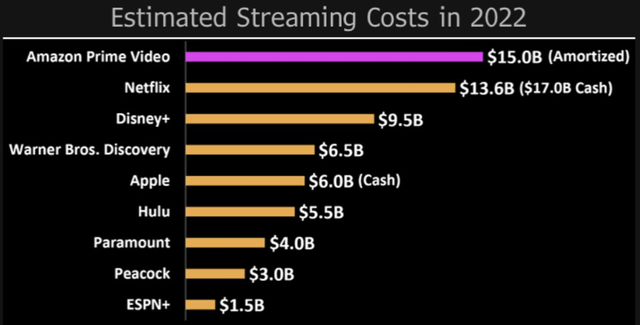
The success of Amazon Prime is underpinned by the multiple benefits it offers alongside fast and free delivery, making the subscription service increasingly sticky, and thereby keeping the network effect rolling. However, these packaged Prime benefits are indeed capital intensive to maintain. For instance, Amazon will far exceed most of its video streaming competitors this year in terms of content spend, estimated to be $15 billion.
The company is spending $1 billion annually on its 11-year streaming rights for NFL Thursday Night Football, a contract it won in 2021. Offering lucrative Prime benefits to encourage membership/ renewal is indeed expensive, putting pressure on profit margins.
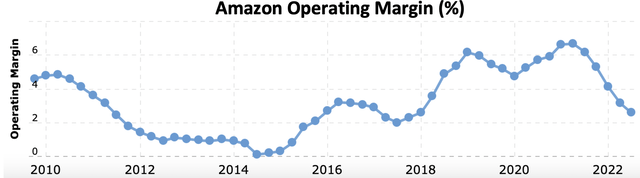
Amazon’s operating margin has been on a declining trend since Q2 2021, falling to 2.58% in Q3 2022. Note that Amazon’s income statement also reflects financial performance/ activity of other divisions like AWS. Nevertheless, persistently enhancing Prime benefits to embolden the Prime network effect is indeed capital intensive, hence compressing profit margins and undermining the P/E multiple the stock is able to command.
The core of Amazon’s moat is its industry-leading fulfillment capabilities, which enables it to effectively facilitate its fast delivery services for Amazon Prime members. Amazon’s fulfillment and logistics prowess is driven by a hard-working human labor force working under intense time pressures. Amazon is infamous for exploiting the vulnerability of its workers, including repeated cases of wage theft and unacceptable working conditions. While Amazon has been offering to rectify these issues, the recurrence of these instances is indeed reflective of Amazon’s unethical business practices. A persistence in discontent laborers raises the risks of labor strikes, undermining Amazon’s ability to fulfill its Prime delivery promises, and also impairs Amazon’s brand image from an ethics standpoint, which may dishearten digital merchants from working with Amazon going forward if these practices aggravate in severity. Cases of wage theft are also discouraging from the perspective of ‘Socially Responsible Investing’, whereby investors seek to avoid profiting from unethical business practices that contradict their moral principles and religious values.
Summary
The Amazon Prime network effect has been evolving for almost two decades. The growing Prime subscription base remains an appealing attribute of selling on the Amazon marketplace. Accessibility to Amazon’s Prime benefits like industry-leading fulfillment and its loyal subscriber-base through ‘Buy with Prime’ could indeed encourage certain merchants to list products off-site, as it subdues the need to continue listing on Amazon’s highly-competitive marketplace. That being said, the Amazon platform continues to offer key advantages like a recurring stream of loyal web visitors, which moderates the risk of merchants completely de-listing from Amazon. The maintenance of Amazon’s Prime network effect relies on heavy capital expenditure, which may undermine profitability, and a strenuous fulfillment & logistics labor force that continues to be the source of legal troubles amid unethical business practices.
Any buying and selling decisions in Amazon stock should take into consideration all business divisions (including AWS and hardware) together. As this article solely focuses on the Third-party sellers/ Prime network, a neutral ‘hold’ rating will be assigned to the stock.


Be the first to comment